

In the table below you'll find several examples of how the irregular past tense and past participles are formed. Many irregular past participles end in -en, but, similarly to the past tense, they can also end in -t, -ck, -d, -e, -g, or -ght. For example, many irregular past participles require you to add an -en, -n, or -ne ending ( drive → drive n). However, the vowel or ending is often (but not always) different from the past tense form. Just like the irregular past tense, irregular past participles can be formed by changing a vowel, adding a new ending, or doing both. Often, when the base ends in -ck, -e, -g, -ght, or -n, the past tense will keep that final letter or set of letters. Sometimes you'll add -d ( sell → sol d) or -ght ( catch → cau ght) instead. One of the most common irregular past tense endings is -t ( sweep → swep t). Eat, for example, turns into at e in the past tense. Other verbs require you to change a vowel and add a new ending. The verb dr ive, for example, changes to dr ove in the past tense. With the irregular past tense, it is common for a vowel in the middle of the verb to change instead of the verb's ending.

Let's take a closer look at how the irregular past tense and past participles are formed. You'll learn more about this concept later in this lesson. Most irregular verbs follow a specific pattern.Beg an (base form, beg in) and fr oze (base form, fr eeze) are a two good examples. It's very common for a vowel (or pair of vowels) to be different from the base form.Some examples are at e, fough t, swa m, and give n. They all have one important characteristic in common: they almost never end in -ed.

Here are a few basics you'll want to remember about the irregular past tense and past participle forms. Past participle (Perfect tense) It is formed by adding -ed at the end of the base form of regular verbs and with irregular verbs we cannot determine what to add at the end of the base form, so we have to memorize them.Irregular Past Tense and Past Participles Simple past tense: It is formed by adding -ed at the end of the base form of regular verbs and with irregular verbs we cannot determine what to add at the end of the base form, so we have to memorize them. Present participle (Continuous tense ): It is formed by adding -ing at the end of the base form when we have the continuous tenses or gerund.
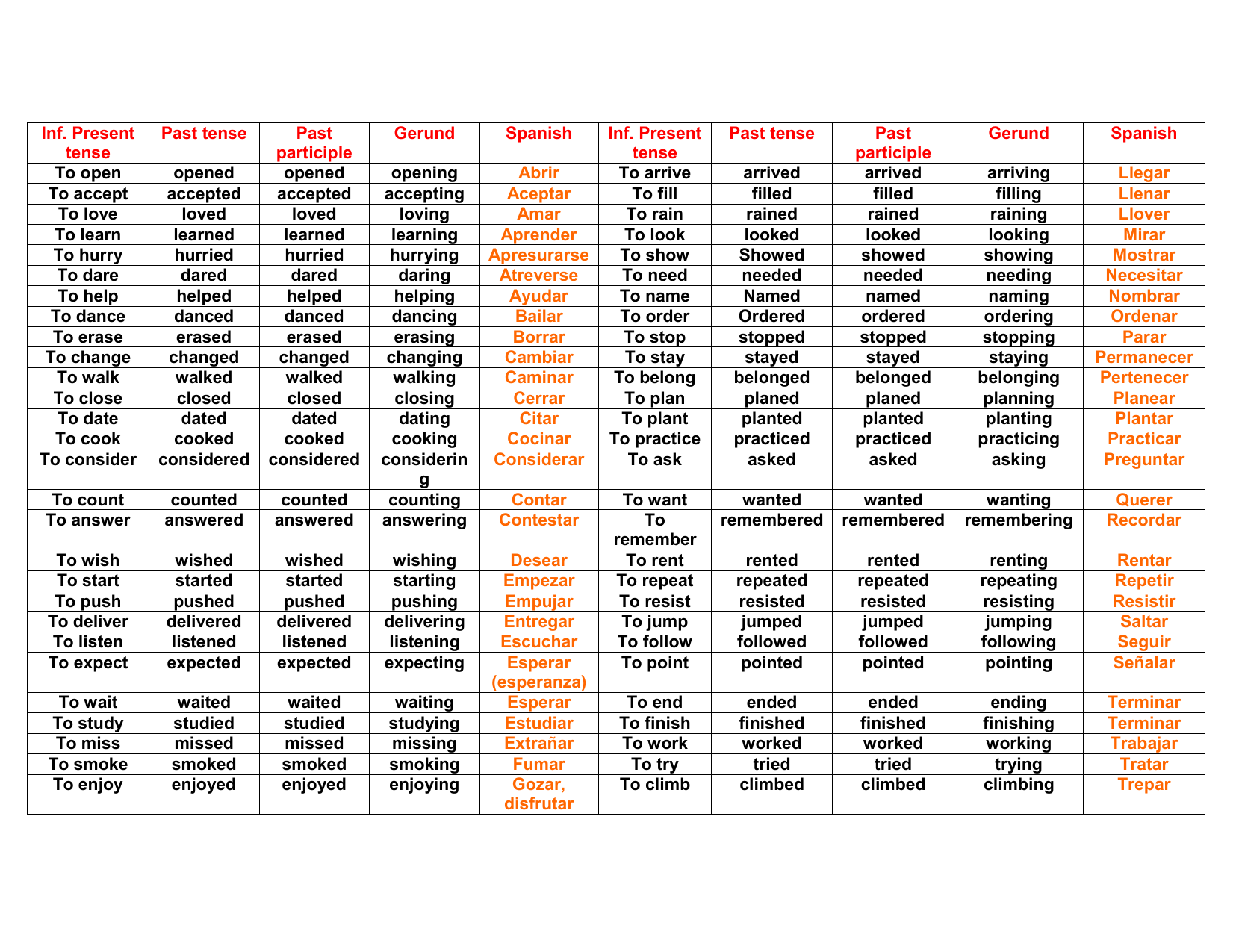
Simple present tense (3 rd person singular): This particular form of the verb is formed by adding s or es at the end of the base form when we have 3rd person singular as a subject. This is the verb that is often used to look up the dictionary. Before getting into learning the forms of verbs we need to understand the terms we have used in the tables of verb forms.īase form: It is the root form of a verb without any specific ending -ed, -ing etc.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
